28.4k views
Root cause analysis (RCA) is a systematic approach to problem-solving, and it requires gathering information from multiple sources and analyzing data collected over time. In other words, it’s a way to uncover hidden patterns and trends within large amounts of data.
Companies often use root cause analysis to help them avoid similar problems in the future. This article will discuss the basics of root cause analysis, including its benefits and limitations.
Root cause analysis (RCA) is a technique used to identify the underlying causes of a problem or issue. RCA aims to determine why something went wrong and then take corrective actions to prevent future occurrences.
RCA has become a widely accepted method of identifying problems within organizations. In recent years, it has also gained popularity amongst businesses looking to improve their operations.
RCA can be applied to any situation where a problem occurs. This includes both internal and external issues. For example, RCA can analyze customer complaints, employee performance, organizational structure, and others.
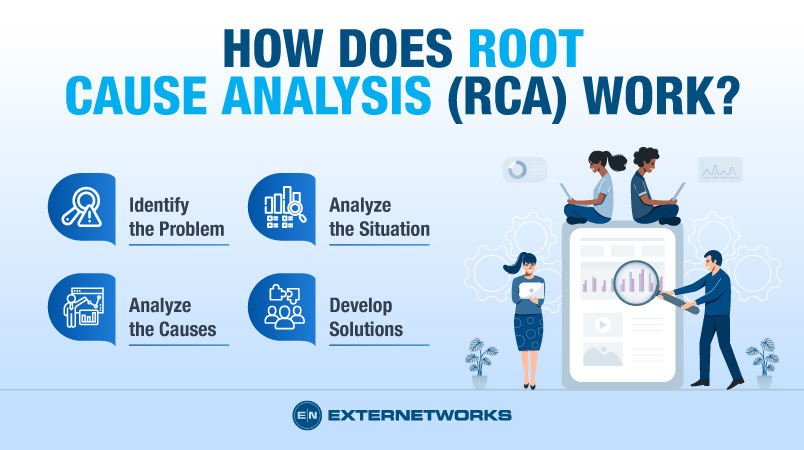
The basic steps involved in performing an RCA are:
Identify the Problem – Identifying the problem is the first step in performing an RCA, and it involves gathering information about what happened and who was responsible for making that happen.
Analyze the Situation – Once you have identified the problem, you need to understand how the problem occurred. You will want to gather as much information as possible about the incident.
Analyze the Causes – After you have gathered all the necessary information, you need to start analyzing the cause of the problem. Multiple factors may contribute to the problem, and by understanding these factors, you can better prepare yourself to solve the problem.
Develop Solutions – Finally, once you have analyzed the causes, you must develop solutions to fix the problem. These solutions should address each of the contributing factors.
There are several reasons why organizations use root cause analysis. Here are some of the most common ones:
Improve Quality – When performing RCA , you identify the actions that led to a particular outcome. This allows you to change your processes, so they don’t repeat the same type of errors.
Reduce Costs – If you have many incidents, performing RCA can help reduce costs. For example, if you find that a certain product has a high rate of defects, you might decide to stop using that product. In addition, you can analyze the root causes of an cyber incident to see what steps you can take to prevent similar issues from happening again.
Identify Trends – If you perform root cause analysis regularly, you can spot company performance trends. You can then use this information to improve your business strategy.
Identify Potential Problems – If you know how a particular issue occurred, you can better prepare yourself for potential problems in the future. For example, if a customer service representative makes a mistake, you can train her to handle similar situations more effectively.
Although root cause analysis is a powerful tool, it has some limitations. Here are three of them:
Time Required – It takes time to perform root cause analysis, and the amount of time required depends on the organization’s size and the problem’s complexity. However, even small companies can benefit by performing rca once or twice yearly.
Cost – Performing RCA requires resources such as people, equipment, and software. Depending on the project’s scope, you may need additional staff members to complete the process.
Accuracy – Even though root cause analysis helps you pinpoint the exact source of an error, it doesn’t always provide accurate results. Sometimes, multiple factors contribute to a particular outcome, and in these cases, you won’t be able to determine which one was responsible for the error.
In conclusion, Root cause analysis is a powerful tool that can help you find the source of problems and prevent them from happening again. It’s also a great way to learn about your business so you can make changes that improve performance.
