28.4k views
The importance of data privacy has increased over time. In the past, people shared their personal information without thinking twice. Nowadays, however, they want to control who sees their private details, and they also want to ensure that no third party gets access to their sensitive information.
Data privacy isn’t something new. People are becoming more aware of the risks of giving out too much information. They want to protect themselves from identity theft and cyber crimes.
Data privacy is an aspect of data protection that focuses on keeping your data safe from unauthorized access and manipulation.
Data Privacy is typically associated with appropriately managing personal data or personally identifying information (PII) such as names, addresses, and credit card details. However, the concept also applies to other sensitive data types, including financial and intellectual property. Industry standards and regulations often govern data privacy and security initiatives, as well as the legal mandates of various governing bodies and jurisdictional authorities.
The importance of data security is directly related to the value of data. The growing data economy is driving businesses across all industries to collect and store more information from more sources than ever.
Today, we live in an era where data is arguably the most valuable asset any organization can own. Companies find tremendous value in collecting, sharing, and using data about customers, users, or clients, especially from social media channels. Transparently requesting permission to collect, share, and use data about people is crucial to building trust with those individuals who naturally expect privacy as one of our fundamental rights.
Managing data to ensure regulatory compliance can be just as challenging as managing your own data. A business may have legal obligations to collect, manage, and protect personal information, and non-compliance can lead to fines and penalties. If the business becomes a victim of a cyber attack, revenue loss and lost customer trust could also be devastating.
Proper data privacy compliance can yield four major benefits for a business, including:
Lower storage costs: Storage costs are reduced because companies that make rational decisions about how much data they should keep and where they should keep it eliminate unnecessary data collection and storage.
Better data use: Businesses should make better use of data, and they should collect and retain better quality data. That means they should have better analytics.
Better business reputation and brand: Businesses should consider how they protect customer information. Data breaches can cause significant reputational harm to businesses, so companies must take steps to prevent such incidents from occurring. Companies should also ensure that they follow best practices for protecting customer data, including implementing strong security measures and conducting regular audits to identify potential vulnerabilities.
Regulatory compliance: Data protection compliance can help companies avoid legal action and financial penalties for data security issues.
Some key examples of cloud data privacy issues can be:
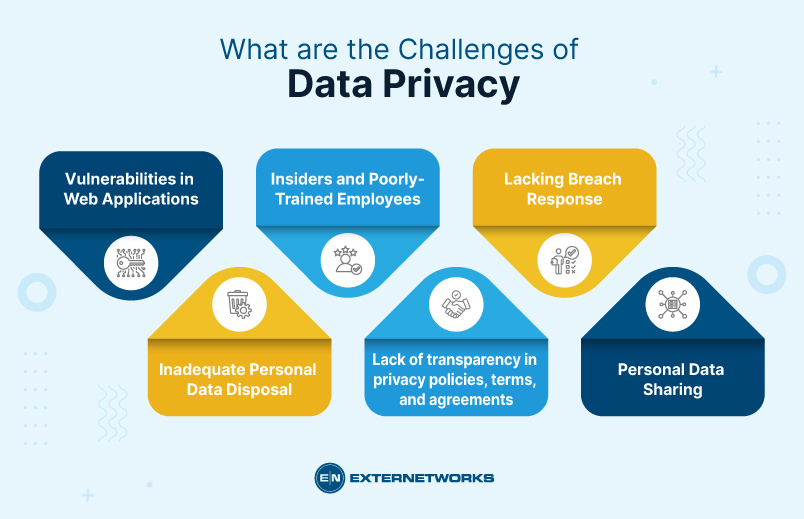
Data privacy is related, but not the same, as data security. They both have overlapping requirements, but they also have distinct differences. For example, data security requires encryption, whereas data privacy does not. Also, data security requires authentication, whereas data privacy does require authorization.
Privacy protects people’s personal information from being used without their consent, and security prevents unauthorized users from accessing your computer system or network.
Data privacy, by comparison, focuses on information about individual users. Privacy rules govern what kinds of personal information may be collected, who may see it, how it may be used, and whether any special protections should be applied. Businesses must ensure that only authorized persons within the company have access to user data, that such data is shared only with trusted partners, and that no sensitive information is released to unauthorized parties.
In conclusion, data privacy is about protecting individuals’ private information and ensuring that companies collect, use, share, and disclose personal information responsibly. Companies need to take steps to protect the privacy of their customers, employees, vendors, and other stakeholders. The key to doing so is to develop and enforce a comprehensive data privacy policy.
