28.4k views
An optical network is a telecommunication infrastructure that uses light waves to transmit data over long distances.
The two main types of optical networks are Passive optical networks (PONs) and Active optical networks (AONs). PONs are usually installed at the central office or head end of the service provider. They consist of a single fiber optic cable that connects multiple customer premises equipment (CPE) devices.
AONs are typically deployed at the remote node where they connect multiple CPEs.
Optical networks are becoming increasingly important because they provide high bandwidth transmission capabilities.
In addition, they offer better reliability and security compared to copper wire networks. This means that companies are investing heavily in them.
As a result, there has been a rapid growth in the number of optical networks being deployed around the globe.
This article will look into Active Optical Networks (AON), and Passive Optical Networks (PON), and the major difference between AON Vs PON.
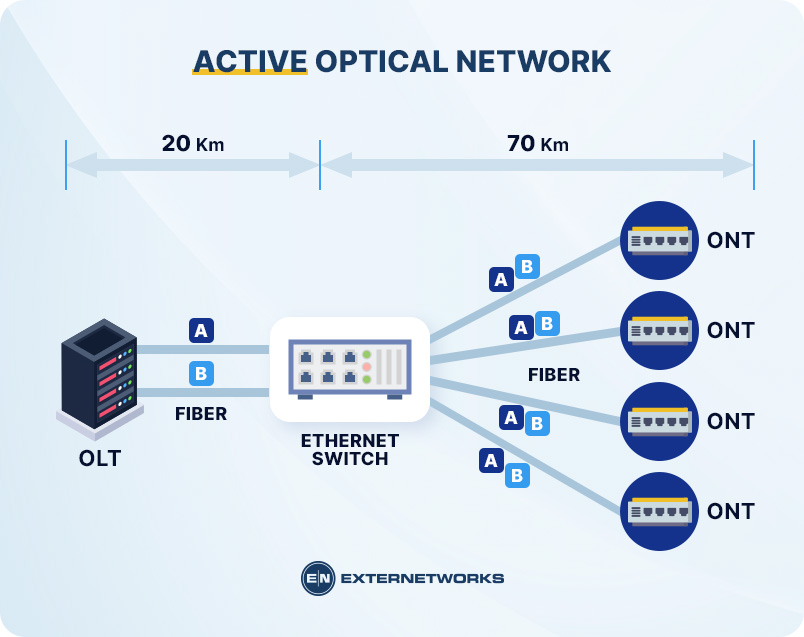
Active optical networks are also known as hybrid networks. Hybrid networks combine active and passive components. Unlike passive networks, active networks can change routes depending on the amount of traffic being sent. Because active networks use both active and passive components, they are more complex than PON networks.
In an active optical network, there are three main types of devices. Amplifiers, transponders, and modulators. The combination of these devices allows for more complex communication schemes.
Amplifiers
Amplifiers increase the amount of light traveling through an optical fiber cable. Amplifiers can be either analog or digital. Analog amplifiers are much cheaper than digital amplifiers, and Digital amplifiers use lasers instead of LEDs to create light. These amplifiers are typically found in large buildings such as data centers and hospitals.
Transponders
Transponders convert signals from one format into another. For example, if you want to send a television signal over a phone line, you need a converter to change it into a telephone signal. You could then plug your telephone directly into the wall jack.
Modulators
Modulators are similar to transponders except that they work in reverse. Instead of converting a signal from one format to another, modulators convert an optical signal from one wavelength to another. For example, you might want to transmit a red laser beam over a blue fiber. You would use a modulator to convert the red laser beam into a blue laser beam.
There are three main types of active optical networks: point-to-point, ring, and mesh.
Point-To-Point
This type of network connects two devices together. It works by splitting up the light into different wavelengths. One part goes to the first device, while the second part goes to the second device.
Ring
This type of network is also known as a star topology. It works by connecting each node to every other node. Each node then sends its own information to the next node until it reaches the last node.
Mesh
This type of network works similarly to a ring network. However, instead of connecting each node to every node, it connects each node to some nodes. Then, those nodes connect to other nodes. In this way, it creates a path through the network that allows all of the nodes to communicate.
AON networks provide several benefits over their passive counterparts. Here are some of them:
Faster speed – Because active optical networks do not rely on passive components, they can move data faster.
Greater reliability – Unlike passive optical networks, active optical networks do not require any power consumption. Therefore, if something happens to the power supply, the network will still work.
Lower costs – Active optical networks are less expensive because they don’t need to be powered. Also, since they have no passive components, they won’t break down as passive ones would.
More flexible – Since AON network doesn’t depend on passive components, they can handle more complicated situations than passive ones could.
While active optical networks offer several advantages over passive optical networks, they also have certain disadvantages. Some of these drawbacks include:
Higher maintenance cost – Although active optical networks don‘t need power, they still require regular maintenance. If you want your network to run smoothly, you must ensure that everything is working correctly. Otherwise, you might end up spending too much money fixing things.
Higher installation cost – While AON network is easier to install than passive ones, they also cost more, and you will have to pay extra for the installation services.
Lower scalability – While AON networks can scale better than passive ones, they cannot grow indefinitely. So, if you plan to increase the amount of traffic going through your network, you should consider using passive optical networks instead.
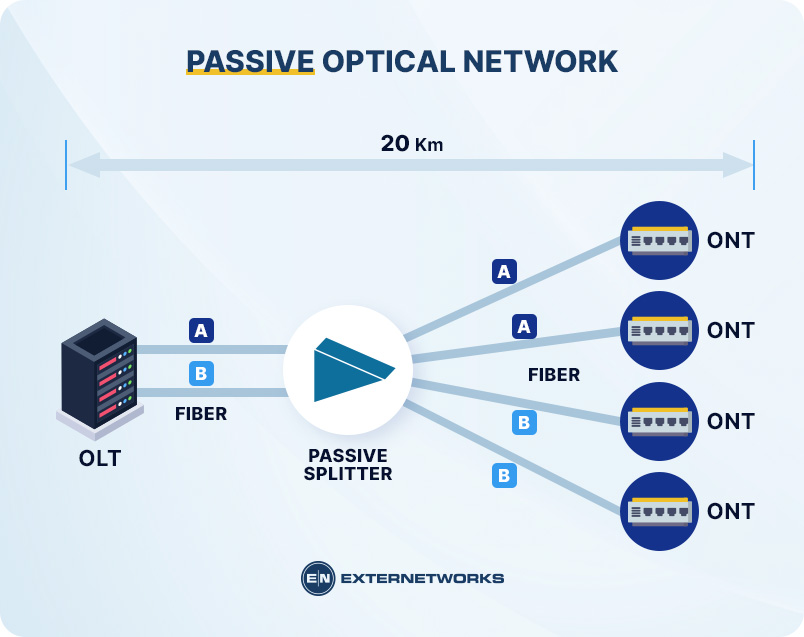
A passive optical network is a form of point-to-point communication. In these networks, information travels along a single path from a source to a destination. All of the devices along this path are passive. Passive devices include optical splitters, couplers, and repeaters. If you were to remove any of these devices from a passive network, the signal would still travel down the same path.
Passive optical networks are very common today because they are easy to set up and maintain. Most homes and businesses already have some sort of passive network installed.
There are four main types of passive optical networks: 1+1, 2+2, tree, and hybrid.
1+1
This type of PON works by using just one wavelength per line, and all of the lines share the same wavelength.
2+2
This type works by dividing the wavelengths into two groups. Each group contains half of the wavelengths, and they are then sent to separate locations.
Tree
This type of PON network by creating multiple levels of connections. At the lowest level, there are only two nodes, and as the number of nodes increases, they branch off into smaller branches. Eventually, the tree becomes so large that it forms a single connection.
Hybrid
This type of PON network combines both active and passive elements. For example, it may use a combination of 1+1 and 2+2 systems.
The passive optical network was first introduced back in the 1980s. They were designed to replace copper wire-based LANs. At the time, they offered higher speeds compared to what was available before. But, today, they are considered obsolete. In fact, new technologies such as Ethernet are now being used to provide high-speed connectivity.
However, passive optical networks do have their own set of benefits. Here are some of the advantages of using PON Network:
Easy Installation – The biggest advantage of passive optical networks is that they are easy to install. Unlike active optical networks, passive optical networks don’t need any additional hardware. All you need is a cable and a device called a splitter.
Lower Cost – PON Networks are cheaper than active components. Since they don’t need power, they don’t require any special wiring. Also, since they don’t have any moving parts, they are less prone to failure.
Better Scalability – Passive optical networks offer great flexibility when it comes to scaling. Because they don’t rely on electricity, they can be scaled easily without having to worry about running out of space.
Although passive optical networks are very flexible, they aren’t as fast as active optical networks. That’s why they are not widely used in large businesses.
Also, they are not as reliable as active optical networks. If you compare both types of networks side by side, you will find that passive optical networks are slower and less reliable than active optical networks.
Also, passive optical networks are not suitable for long-distance connections. They are best suited for small to medium-sized networks.
The main difference between active optical networks and passive optical networks(AON vs PON) lies in the way the data travels over the network. With active optical networks, the data travels through the individual fibers themselves. On the other hand, with passive optical networks, the data moves through the air.
In terms of performance, passive optical networks are faster than active optical network. However, this depends on the type of application you are planning to run. For example, if you plan to stream HD videos, then you might get better results from active optical networks.
In terms of cost, passive optical networks are much more affordable than active optical networks. But again, this depends on the kind of project you are working on. If you are building a new network, then you won’t have to spend too much money.
Passive optical networks are generally considered to be more scalable than active optical networks. This means that they are easier to scale up or down depending on how much traffic you expect to generate.
However, active optical networks are usually more robust than passive optical networks. This is because they don’t depend on any external power source. As such, they are able to withstand power fluctuations and disruptions better than PON passive optical networks.
Another advantage of active optical networks is that they provide higher dedicated bandwidth. In fact, they can carry multiple wavelengths of light simultaneously. This makes them more efficient than passive optical networks. Also, it allows them to support greater numbers of users.
In conclusion, When choosing between active optical networks and passive optical networks, you should consider your needs and requirements. You should also think about whether you want to use them for short-term or long-term projects.
If you are looking for a solution that offers low latency, then you should opt for active optical networks. On the other hand, if you are looking for a system that provides better reliability and scalability, then you should choose passive optical networks. These systems are good for companies that operate in highly dynamic environments.
